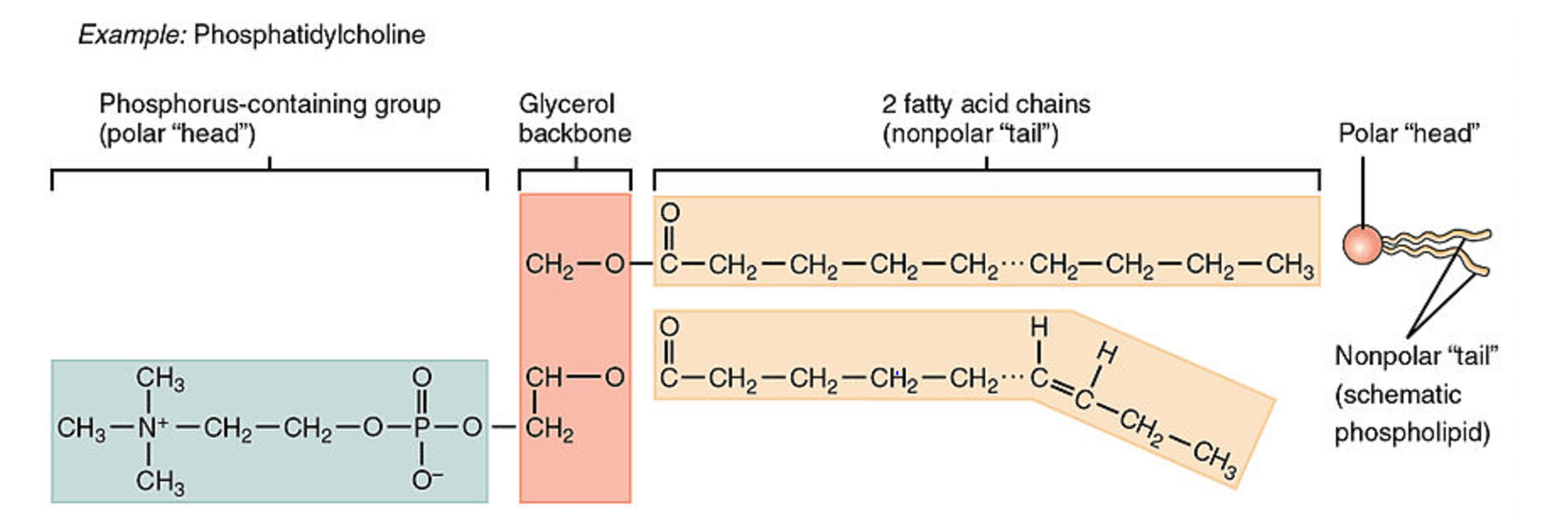
Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids . Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a. They include fatty acid, glycerol, sphingosine and steroid. Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. glycerol and fatty acids. lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. A fat molecule consists of two main components: hydrolysis product of simple and compound lipids is called derived lipids. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three. a fat molecule consists of two main components: the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids.
from www.expii.com
Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a. A fat molecule consists of two main components: hydrolysis product of simple and compound lipids is called derived lipids. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids.
Chemical Structure of Lipids — Overview & Types Expii
Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. hydrolysis product of simple and compound lipids is called derived lipids. Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. A fat molecule consists of two main components: glycerol and fatty acids. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a. a fat molecule consists of two main components: They include fatty acid, glycerol, sphingosine and steroid. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lipids, Membranes & the First Cells PowerPoint Presentation ID Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. a fat molecule consists of two main components: a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. They include fatty acid,. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From thebiologynotes.com
Fatty Acids Definition, Classification, Types, Functions Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. A fat molecule consists of two main components: Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. hydrolysis product of simple and compound lipids is called derived lipids. lipids are an essential component. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From philschatz.com
Lipid Metabolism · Anatomy and Physiology Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three. lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. They include fatty acid, glycerol, sphingosine and steroid. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. The structure is. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lipids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6999007 Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. A fat molecule consists of two main components: hydrolysis product of simple and compound lipids is called. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From chemicaldb.netlify.app
Fatty acid and glycerol Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. glycerol and fatty acids. a fat molecule consists of two main components: a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. hydrolysis product of simple and compound lipids. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From www.slideshare.net
LIPIDS Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a. lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. a fat molecule consists of two main components: Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh). Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From spmbiology.blog.onlinetuition.com.my
4.4 Lipids SPM Biology Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. A fat molecule consists of two main components: Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a. . Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Biomolecules PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2142839 Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. They include fatty acid, glycerol, sphingosine and steroid. lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three. The structure is. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Lipids Microbiology Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a.. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lipid structure, function and chemistry PowerPoint Presentation Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. The structure is typically made of a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (hydrophobic), and a. a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From www.expii.com
Chemical Structure of Lipids Expii Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids They include fatty acid, glycerol, sphingosine and steroid. a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From www.researchgate.net
Representative structure for each lipid category. The LIPID MAPS Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids A fat molecule consists of two main components: lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. They include fatty acid, glycerol, sphingosine and steroid. lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups.. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Lipids PowerPoint Presentation ID6638022 Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. A fat molecule consists of two main components: Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. They include fatty acid, glycerol, sphingosine and steroid. glycerol and fatty acids. the most ubiquitous. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Lipids Biology for Majors I Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. hydrolysis product of simple and compound lipids is called derived lipids. a fat molecule consists of two main components: Glycerol is an organic compound. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From pt.slideshare.net
Lipids Chemistry Structure & Function Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids lipids are an essential component of the cell membrane. lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. glycerol and fatty acids. They include fatty acid, glycerol, sphingosine and steroid. Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Lipids Boundless Anatomy and Physiology Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three. hydrolysis product of simple and compound lipids is called derived lipids. lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls of the glycerol. lipids are. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From pmgbiology.wordpress.com
Biological Molecules A* understanding for iGCSE Biology 2.5 2.6 2.7 Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three. the most ubiquitous lipids in cells are the fatty acids. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. a fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.
From www.biologyexams4u.com
Biochemistry notes Classification of Lipids Differences between Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids Found in fats, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and serving as as membrane anchors for. glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. hydrolysis product of simple and compound lipids is called derived lipids. lipids used for energy storage are the glycerolipid, triacylglycerol (tag), where each of the three hydroxyls. Lipids Structure Glycerol And Fatty Acids.